12 Aug Spinal Cord Stimulator Implant for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
FAQs on Spinal Cord Stimulator Implant for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
What is diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy occurs due to damage to the peripheral nervous system, which comprises of motor and sensory nerves that connect the brain and the spinal cord with rest of the body. When prolonged exposure to high blood glucose levels causes the disorder, it is called diabetic peripheral neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy.
What are symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
Diabetes-related complications over an extended period of time damage peripheral nerves going to upper and lower extremities. This leads to abnormal sensations in arms, hands, legs, and feet, such as
- tingling
- burning sensation
- numbness
- throbbing
- failure to notice minor cuts, sores, blisters in hand and feet
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy also impacts sensory and motor nerves feeding digestive and reproductive organs. It enhances the risk of ulcer and gangrene in lower extremities and foot amputation.
What causes diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
Prolonged diabetic conditions lead to complications that inhibit blood-oxygen supply to peripheral nerves connecting extremities. This damages peripheral nerves and causes inflammation of the nerves resulting in the loss of functional capacity.
What is the prevalence of diabetic neuropathy?
About 65 percent of those with diabetes face the risk of suffering from peripheral neuropathy. It is common in people with diabetes for over 25 years. Scientific evidence suggests that the risk increases with age and duration of diabetes.
How to treat diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
There is no cure or prevention of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. However, advanced medical technology offers various ways to manage the disorder and prevent its symptoms from affecting your life.
Spinal cord stimulation is an effective way to overcome pain and discomfort associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
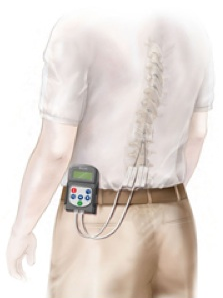
What is a spinal cord stimulator?
A spinal cord stimulator is a medically approved electrical device implanted in the spinal area. It has microelectrodes emitting electric signals, which interferes with pain sensation transmission. The device can be customized to deliver electric pulses according to individual patient requirements.
How does a spinal cord stimulator work?
Spinal cord stimulator follows a specific pain relief method called neuromodulation. Electrical impulses emitted from the device affect the nerve activity, especially their firing pattern and excitability. This has its effect on the pain sensation transmission to the brain. The pain sensation is inhibited and non-pain sensation gets more attention by brain receptors. This ensures relief from pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
How does spinal cord stimulation relieve pain caused by peripheral neuropathy?
The stimulator delivers electrical impulses to the spinal area and these impulses obstruct pain signal transmission by nerve fibers. Thus, spinal cord stimulation inhibits or masks pain sensation. This allows non-pain sensation to get more attention and patients no more experience pain in arms, hands, legs, and feet linked to diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Who should undergo spinal cord stimulator implant to treat diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
Anyone with diabetic peripheral neuropathy can have positive results with spinal cord stimulation. However, this is an invasive procedure and all are not fit enough to undergo the implant surgery. The most suitable candidates for spinal cord stimulator implant must have
- good physical and mental health
- severe diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- chronic pain from diabetic peripheral neuropathy for more than a year
- no effective relief from medical and conservative therapies
- confirmation of diabetic peripheral neuropathy as source of pain
- no painkiller dependency
- no ongoing infection
- not implanted with any electromagnetic medical device
How effective is spinal cord stimulation therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy?
Those undergoing spinal cord stimulation therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy do not need any pain medication and can thus avoid developing dependency on drugs. It assures better, long-term relief without side effects. Research evidence suggests at least 70 percent pain relief over 15 years from chronic neuropathic pain when a patient is treated with spinal cord stimulation therapy.
A 2011 review found at least 63 percent success rate of spinal cord stimulation in ensuring more than 50 percent pain relief in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. According to another study, the therapy vastly improves the condition of 85 to 90 percent patients with neuropathic pain.
How long does the device last?
Once implanted the device offer pain relief from more than 20 years.
Is trial spinal cord stimulator implant is mandatory?
Spinal cord stimulation trial is essential to check if the device offers substantial benefit to a diabetic peripheral neuropathy patient without any side effect. The main implant procedure is invasive and expensive. A trial run saves one from such costly affairs if the device is found to be of no significant benefit for him or her.
What is done during the SCS trial?
Doctors check the fitness of the patient for the procedure. Intravenous sedation is used to tranquilize the patient. The skin above the lumbar area is numbed and a needle is inserted. A catheter is put inside the needle. The spinal cord stimulator is connected with the catheter and programmed to deliver electrical impulses as per the patient requirement. The device is fastened with a belt wrapped around the patient’s waist.
How long does it take?
The trial implant takes about 60 to 90 minutes. However, the SCS in the trial mode goes on for a week and the diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain relief is assessed.
How is a spinal cord stimulator implant performed?
If the patient experiences at least 50 percent pain relief from diabetic peripheral neuropathy during the trial period, he or she is considered for permanent spinal cord stimulator implant. Patients have the option to choose between spinal cord stimulators with internal and external batteries.
General anesthesia is used during the implant surgery. A small space is created by clearing the bony areas next to the lower spine. The programmed device is securely placed and connected to a catheter. The catheter makes way through soft tissues to reach the spinal area.
Once the placement is complete, the device is switched on and delivery of electrical impulses is tested. The incisions are closed and the area is bandaged.
How long does it take?
The surgery takes about 2 to 3 hours.
What should I expect after the spinal cord stimulator implant?
Patients experience immediate pain relief from diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Actual results are experienced only after 72 hours. There will be soreness at the surgery site for a few days. Patients have to take certain post-surgical precautions to ensure fast healing and avoid complications.
What are post-surgical precautions?
- Have rest for a week
- Avoid any movement that may put pressure on the surgical site
- Avoid twisting or bending for 6 weeks
- No stressful work for 6 weeks
How long is the post-implant recovery?
Most patients return to work or resume regular work after a week. However, intense workouts or stressful activities must be avoided for 6 weeks.
 Do I need to change spinal cord stimulator implant after some years?
Do I need to change spinal cord stimulator implant after some years?
No, once implanted, the device lasts for more than 20 years. Only thing you need to change after a few years is batteries. You can go for a device with internal or external batteries.
How often is the battery changed?
Spinal cord stimulator batteries last between 5 to 10 years.
When can I experience pain relief?
Patients begin to experience pain relief from diabetic peripheral neuropathy as soon as the spinal cord stimulator implant is performed. However, the initial results vary in the first three days. The long-term pain relief benefit is experienced only after the third day.
What are side effects of spinal cord stimulator implant?
Spinal cord stimulator implant is safe. However, the surgery carries the risk of bleeding, nerve damage, and post-surgical complication if the standard surgical procedure and precautions are not followed.
References
Pluijms WA, Slangen R, Joosten EA, et al. (2011). Electrical spinal cord stimulation in painful diabetic polyneuropathy, a systematic review on treatment efficacy and safety. Eur J Pain, 15(8):783–788.
Slangen R, Schaper N, Faber C, et al. Spinal Cord Stimulation and Pain Relief in Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Prospective Two-Center Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2014 Sep; DC_140684
Kumar K, Toth C, Nath RK. Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy. Surg Neurol. 1996 Oct;46(4):363-9.
Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Gries FA, Ziegler D. Epidemiology of diabetic neuropathy. In: Gries FA, Cameron NE, Low PA, Ziegler D, editors. Textbook of Diabetic Neuropathy. New York: Thieme; 2003. p. 64-82.
Daousi C, Benbow SJ, MacFarlane IA. Electrical spinal cord stimulation in the long-term treatment of chronic painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabet Med 2005;22:393-8.
de Vos CC, Rajan V, Steenbergen W, van der Aa HE, Buschman HP. Effect and safety of spinal cord stimulation for treatment of chronic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 2009;23:40-5.